Learn HTML Using Notepad or TextEdit
Web pages can be created and modified by using professional HTML editors.
However, for learning HTML we recommend a simple text editor like Notepad (PC) or TextEdit (Mac).
We believe in that using a simple text editor is a good way to learn HTML.
Follow the steps below to create your first web page with Notepad or TextEdit.
Step 1: Open Notepad (PC)
Windows 8 or later:
Open the Start Screen (the window symbol at the bottom left on your screen). Type Notepad.
Windows 7 or earlier:
Open Start > Programs > Accessories > Notepad
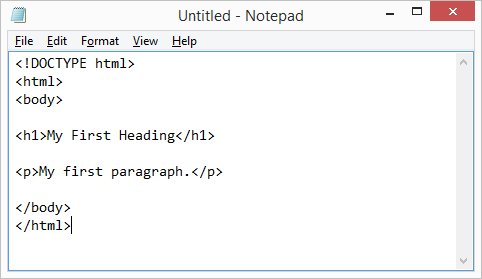
Step 2: Write Some HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>your heading</h1>
<p>your paragraph here</p>
</body>
</html>
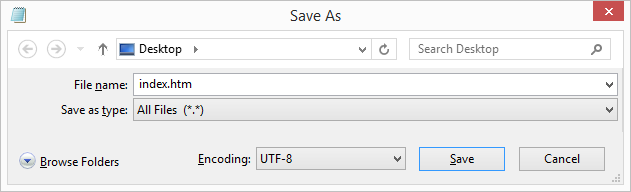
Step 3: Save the HTML Page
Save the file on your computer. Select File > Save as in the Notepad menu.
Name the file "index.htm" and set the encoding to UTF-8 (which is the preferred encoding for HTML files).
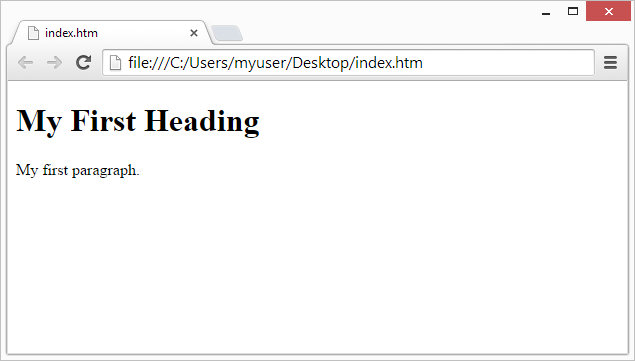
Step 4: View the HTML Page in Your Browser
Open the saved HTML file in your favorite browser (double click on the file, or right-click - and choose "Open with").
The result will look much like this:
like this you can edit and make html page

